WHO: World Health Organization recommends seven NPS for scheduling
GENEVA, Switzerland – December 2022: Since its inception in 2013, the UNODC Early Warning Advisory on NPS regularly provides scientific information to Member States and the World Health Organization (WHO) for the identification of the most harmful, prevalent and persistent NPS in support of review processes for national and international control. The WHO has announced the scheduling recommendations on psychoactive substances reviewed at the 45th Meeting of the WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence (ECDD) held from 10-13 October 2022. In total, nine substances were critically reviewed by the ECDD, seven of which (four synthetic opioids, two synthetic cathinones and one synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist) were recommended for scheduling as listed below, while two benzodiazepines Adinazolam, Bromazolam as well as the medicine Zopiclone (which was subjected to preliminary review) were recommended to be kept under surveillance.
Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs of 1961, as amended by the 1972 Protocol – (Schedule I):
Convention on Psychotropic Substances of 1971 – (Schedule II):
ADB-BUTINACA

All four NPS recommended for scheduling under the 1961 Convention are synthetic opioids. 2-Methyl-AP-237, a piperazine, was reported to the UNODC EWA in 2019 for the first time. The ”nitazenes” Etazene (etodesnitazene) and Protonitazene (propoxynitazene) were reported to the UNODC EWA for the first time in 2020 and Etonitazepyne (N-pyrrolidino etonitazene) in the year 2021. Since 2015, 20 out of 121 reported synthetic opioids to the UNODC EWA have been placed under international control (see Figure 1). A majority of the synthetic opioids placed under international control since 2015 are fentanyl analogues (14). However, all three synthetic opioids placed under international control in 2021 and 2022 and three out of the four synthetic opioids recommended for control by WHO in December 2022 are “nitazenes”, reflecting a diversification in the chemical groups emerging in the illicit market.
Figure 1: Number of synthetic opioids reported to the UNODC EWA, 2015-2022 by international control status (as of November 2022)*
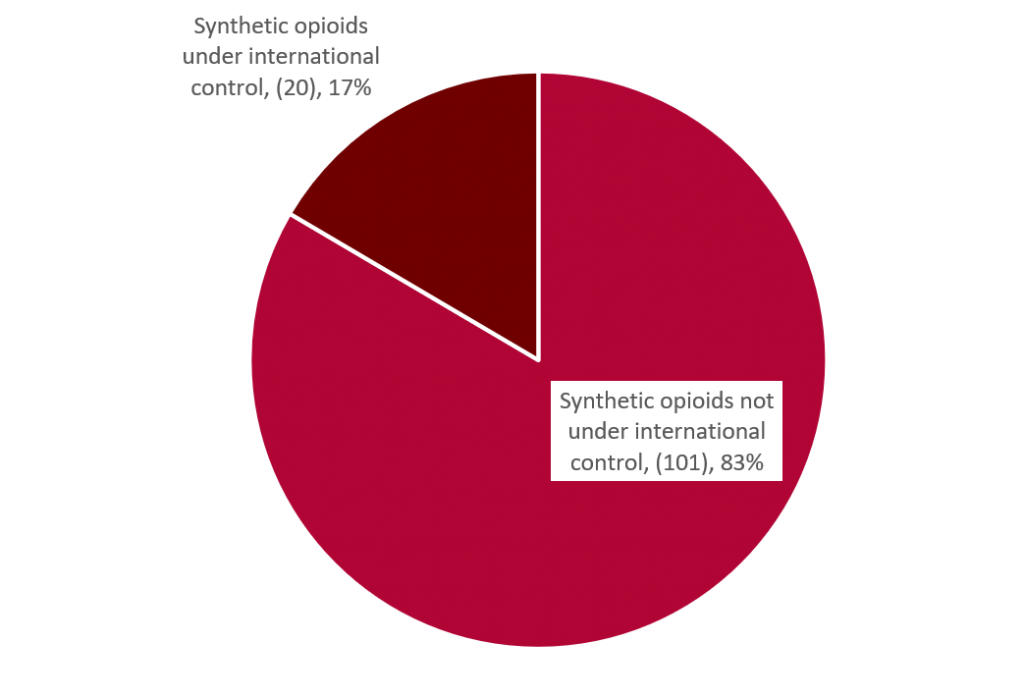
Source: UNODC Early Warning Advisory on NPS.
Note: *Data collection for 2022 not yet complete.
For more information, please see:
45th ECDD List of Substances Under Review
World Health Organization 45th Expert Committee on Drug Dependence
Global SMART Update Vol. 25 “Regional diversity and the impact of scheduling on NPS trends”