UNODC EWA: Benzodiazepine-type substances continue to be a primary NPS threat, particularly in drug driving and post-mortem cases
VIENNA, Austria – August 2023: The UNODC Current NPS Threats Vol. VI presents recent analysis from the UNODC Early Warning Advisory (EWA) on NPS by combining data from NPS identified in seized material with toxicology information from clinical, driving under the influence of drugs (DUID), drug facilitating sexual assault (DFSA) and post-mortem (PM) cases. This allows to identify key developments regarding health threats associated with the use of NPS. Polydrug use continues to be an important feature in NPS casework. Over the data collection period from December 2021 to May 2023, more than 1200 toxicology cases involving 61 individual NPS were reported to UNODC, and trends observed in previous Current NPS threats reports have continued.
Figure 1: New Psychoactive Substance groups reported across main toxicology case types
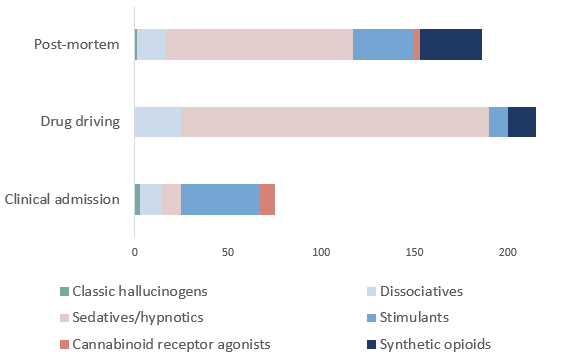
Source: Toxicology portal of the UNODC Early Warning Advisory on NPS, 2023.
Benzodiazepine-type NPS accounted for 52% of the substances reported in post-mortem (PM) cases and 71% of drug-driving (DUID) cases. The most commonly reported substance were etizolam, flualprazolam and flubromazolam. The continuing persistence of benzodiazepine-type NPS from all regions, in DUID and PM cases, continues to highlight the threat potential of this substance group.
Synthetic opioids accounted for 17% of reports in PM cases with notably protonitazene being the most reported substance followed by carfentanil. In comparison to previous reporting periods, there has been an increase in the reporting of nitazenes and a decrease in the identification of fentanyl analogues such as acetylfentanyl.
Regarding the relative contribution that the NPS identified in PM cases had in the fatalities, in 10 cases the NPS was deemed causal to the outcome of the event; four involved the stimulant α-PVP, two involved 4-FMA, two involved bromazolam and one case each involved α-pyrrolidinoisohexanophenone (α-PiHP) and deschloroetizolam.
Figure 2: Substances most often reported in post-mortem cases
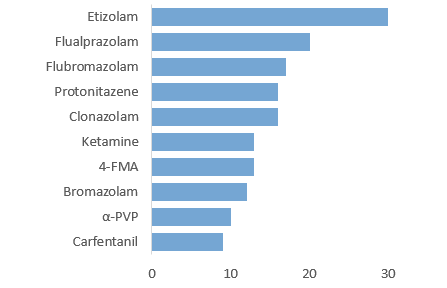
Source: Toxicology portal of the UNODC Early Warning Advisory on NPS, 2023.
For further information please see:
UNODC, Current NPS Threats Volume VI (August 2023)



